StarSBC-6ULL CAN bus example: Difference between revisions
From SomLabs Wiki
Created page with "{{PageHeader|StarSBC-6ULL CAN bus example}} __toc__ This tutorial shows how to send and receive data using CAN bus on StarSBC-6ULL with communication extension board. The def..." |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{PageHeader|StarSBC-6ULL CAN bus example}} __toc__ | {{PageHeader|StarSBC-6ULL CAN bus example}} __toc__ | ||
This tutorial shows how to send and receive data using CAN bus on StarSBC-6ULL with communication extension board. The default Yocto image | This tutorial shows how to send and receive data using CAN bus on StarSBC-6ULL with communication extension board SLH2-comm. The default Yocto image contains all required software tools. | ||
=== Loop test === | === Loop test === | ||
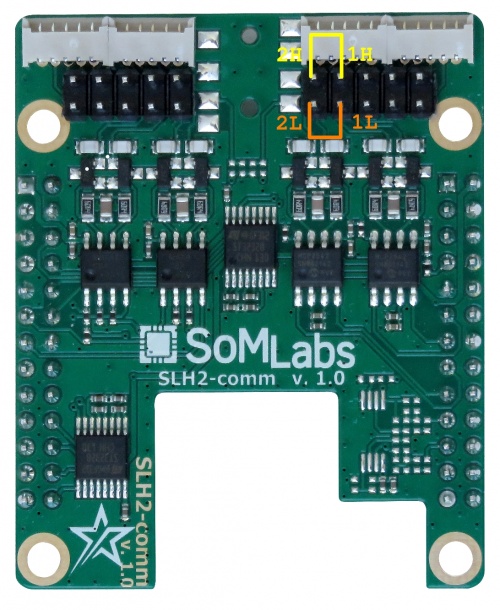
The extension board has two CAN buses available so they may be connected to perform the test in a loop. All signals are available on the J101 connector. They should be connected according to the following table: | The SLH2-comm extension board has two CAN buses available so they may be connected to perform the test in a loop. All signals are available on the J101 connector. They should be connected according to the following table: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| CAN2 H (pin 9) | | CAN2 H (pin 9) | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[File:StarSBC-6ULL-SLH2-can-loop.jpg|center|500px]] | |||
Both CAN buses are already defined in the default module device-tree and are recognized as can0 and can1 network interfaces: | Both CAN buses are already defined in the default module device-tree and are recognized as can0 and can1 network interfaces: | ||
| Line 59: | Line 61: | ||
can0 5E1 [8] 76 16 70 79 13 57 CB 02 | can0 5E1 [8] 76 16 70 79 13 57 CB 02 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
=== CAN/USB converter test === | === CAN/USB converter test === | ||
Latest revision as of 08:58, 13 December 2022
StarSBC-6ULL CAN bus example
This tutorial shows how to send and receive data using CAN bus on StarSBC-6ULL with communication extension board SLH2-comm. The default Yocto image contains all required software tools.
Loop test
The SLH2-comm extension board has two CAN buses available so they may be connected to perform the test in a loop. All signals are available on the J101 connector. They should be connected according to the following table:
| CAN1 signal | CAN2 signal |
|---|---|
| CAN1 L (pin 8) | CAN2 L (pin 10) |
| CAN1 H (pin 7) | CAN2 H (pin 9) |
Both CAN buses are already defined in the default module device-tree and are recognized as can0 and can1 network interfaces:
root@starsbc-6ull:~# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: can0: <NOARP,ECHO> mtu 16 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 10
link/can
3: can1: <NOARP,ECHO> mtu 16 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 10
link/can
4: eth0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 5a:2d:ed:e9:cb:e4 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: sit0@NONE: <NOARP> mtu 1480 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/sit 0.0.0.0 brd 0.0.0.0
6: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 74:7a:90:ca:e4:5d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
The interfaces need to be configured by setting the bitrate and enabled:
ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 ip link set can0 up ip link set can1 type can bitrate 125000 ip link set can1 up
The data may be generated and sent using can-utils tools: cansend, cangen, candump. The following example generates random data and sends it from can1 to can0:
root@starsbc-6ull:~# candump can0 & root@starsbc-6ull:~# cangen can1 can0 384 [8] A5 45 1E 74 C6 35 1A 27 can0 5E1 [8] 76 16 70 79 13 57 CB 02
CAN/USB converter test
This example requires the UCCB CAN/USB converter connected to the StarSBC-6ULL board and PC with Linux host. The Linux host needs also the installed can-utils package, for Ubuntu Linux:
sudo apt-get install can-utils
After connecting the CAN1 H and CAN1 L signals to the converter, a new CAN interface need to be configured on the host side. In this example the converter is recognized in host system as /dev/ttyACM1:
dev@somlabs:~$ dmesg | tail [22206.563301] usb 1-4.1: new full-speed USB device number 58 using xhci_hcd [22206.665197] usb 1-4.1: New USB device found, idVendor=0483, idProduct=5740, bcdDevice= 2.00 [22206.665200] usb 1-4.1: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 [22206.665202] usb 1-4.1: Product: CAN_USB_ConverterBasic [22206.665203] usb 1-4.1: Manufacturer: CANDevices [22206.665205] usb 1-4.1: SerialNumber: 00000000001A [22206.674036] cdc_acm 1-4.1:1.0: ttyACM1: USB ACM device
The following command registers a new CAN bus interface that is attached to the /dev/ttyACM1 device:
sudo slcand -o -s4 -S 115200 /dev/ttyACM1
it sets the bitrate to 125kb and the serial baud rate to 115200.
A new interface should be visible in the system:
dev@somlabs:~$ ip a
8: slcan0: <NOARP> mtu 16 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 10
link/can
It should be set up and then may be used to transmit or receive data using can-utils tools.
On StarSBC-6ULL target:
ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 ip link set can0 up cangen can0
On host:
dev@somlabs:~$ sudo ip link set slcan0 up dev@somlabs:~$ candump slcan0 slcan0 553 [1] 6B slcan0 40E [2] DF D3 slcan0 2D2 [8] 39 21 3A 18 B5 26 E3 2F