StarSBC-6ULL RS485 example: Difference between revisions
From SomLabs Wiki
No edit summary |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{PageHeader|StarSBC-6ULL RS485 example}} __toc__ | {{PageHeader|StarSBC-6ULL RS485 example}} __toc__ | ||
This tutorial shows how to send and receive data using RS485 interface on StarSBC-6ULL with communication extension board. The default Yocto image | This tutorial shows how to send and receive data using RS485 interface on StarSBC-6ULL with communication extension board SLH2-comm. The default Yocto image contains all required software tools. | ||
=== Loop test === | === Loop test === | ||
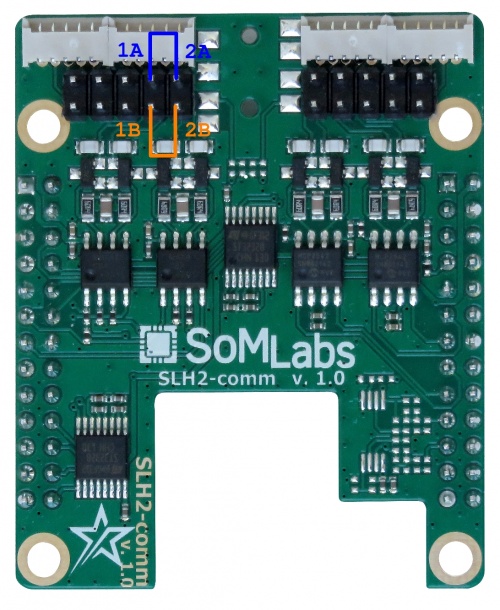
The extension board has two RS485 interfaces available so they may be connected to perform the test in a loop. All signals are available on the J201 connector. They should be connected according to the following table: | The SLH2-comm extension board has two RS485 interfaces available so they may be connected to perform the test in a loop. All signals are available on the J201 connector. They should be connected according to the following table: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Latest revision as of 08:59, 13 December 2022
StarSBC-6ULL RS485 example
This tutorial shows how to send and receive data using RS485 interface on StarSBC-6ULL with communication extension board SLH2-comm. The default Yocto image contains all required software tools.
Loop test
The SLH2-comm extension board has two RS485 interfaces available so they may be connected to perform the test in a loop. All signals are available on the J201 connector. They should be connected according to the following table:
| RS485-1 signal | RS485-2 signal |
|---|---|
| RS485-1A (pin 3) | RS485-2A (pin 1) |
| RS485-1B (pin 4) | RS485-2B (pin 2) |
Both interfaces are already defined in the default module device-tree and are recognized as /dev/ttymxc3 and /dev/ttymxc7 devices. The device files may be used directly for reading and writing and the bitrate may be set using the stty tool:
root@starsbc-6ull:~# stty -F /dev/ttymxc3 9600 raw -echo -echoe -echok root@starsbc-6ull:~# stty -F /dev/ttymxc7 9600 raw -echo -echoe -echok root@starsbc-6ull:~# cat /dev/ttymxc3 & [1] 465 root@starsbc-6ull:~# echo "123" > /dev/ttymxc7 123 root@starsbc-6ull:~#
RS485/USB converter test
This example requires the RS485/USB converter connected to the StarSBC-6ULL board and PC with Linux host.
After connecting the RS485-1A and RS485-1B signals to the converter attached to the PC the stty, cat and echo commands may be used to configure, read and write both ports. In this example the host interface was recognized as /dev/ttyUSB1:
dev@somlabs:~$ dmesg | tail [25050.725905] usb 1-4.1: new full-speed USB device number 61 using xhci_hcd [25050.837144] usb 1-4.1: New USB device found, idVendor=1a86, idProduct=7523, bcdDevice= 2.64 [25050.837146] usb 1-4.1: New USB device strings: Mfr=0, Product=2, SerialNumber=0 [25050.837148] usb 1-4.1: Product: USB Serial [25050.845068] ch341 1-4.1:1.0: ch341-uart converter detected [25050.846044] usb 1-4.1: ch341-uart converter now attached to ttyUSB1
On StarSBC-6ULL target:
stty -F /dev/ttymxc7 9600 raw -echo -echoe -echok cat /dev/ttymxc7
On host:
stty -F /dev/ttyUSB1 9600 raw -echo -echoe -echok echo "123" > /dev/ttyUSB1