How to interface ST L3GD20 gyroscope with the VisionSOM-6ULL
From SomLabs Wiki
How to interface ST L3GD20 gyroscope with the VisionSOM-6ULL
Description
KAmodL3GD20 is a gyroscope module with a L3GD20 chip from STMicroelectronics. It allows to measure angular velocity at ±2000 degrees per second.
Prerequisites
This tutorial is based on a pre-prepared image for VisionSOM-6ULL module. The image is available here: SoMLabs-VisionSOM-6ULL-training-02-2018-sdcard-2gb.zip.
Then you need to write the image file to microSD card. More information you can find in manuals: How to prepare SD Card with Debian 9.2 for VisionSOM-6ULL on Linux or How to prepare SD Card with Debian 9.2 for VisionSOM-6ULL on Windows. Please remember to use a proper image file: SoMLabs-VisionSOM-6ULL-training-02-2018-sdcard-2gb.zip.
| In the ready-to-use OS image, the kernel driver for the gyroscope has already been enabled in the kernel config, and the device has been added to the devicetree. |
If you need more information about how to customize, build and upload Device Tree file, please visit How to customize Debian 9.2 device tree.
Hardware set-up
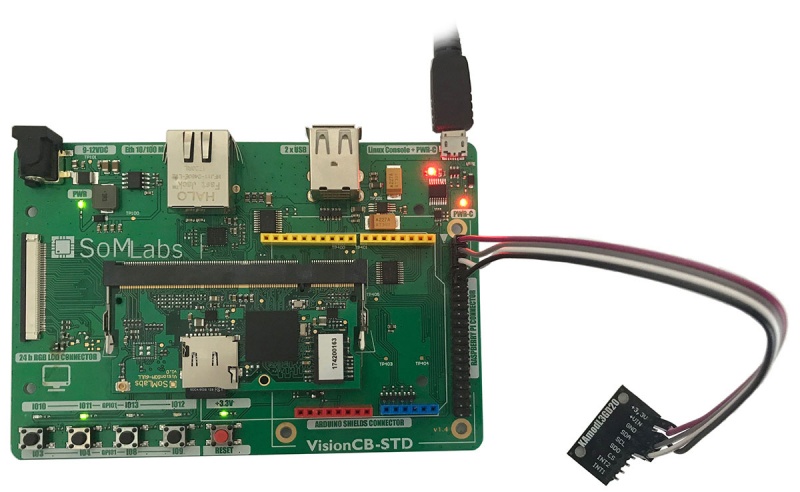
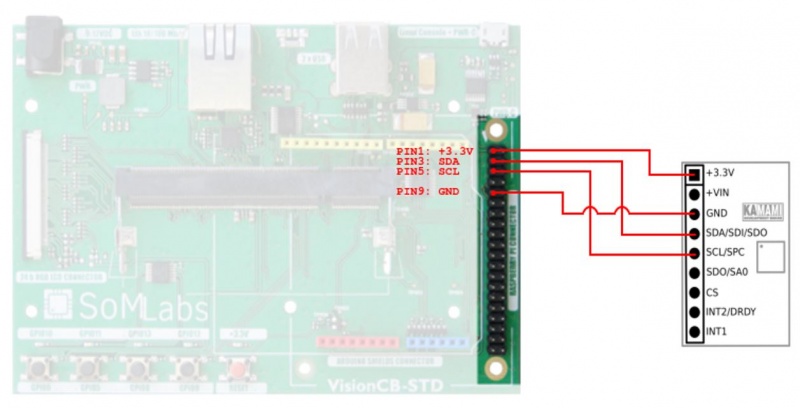
Connect the KAmodL3GD20 module according to the photo below:
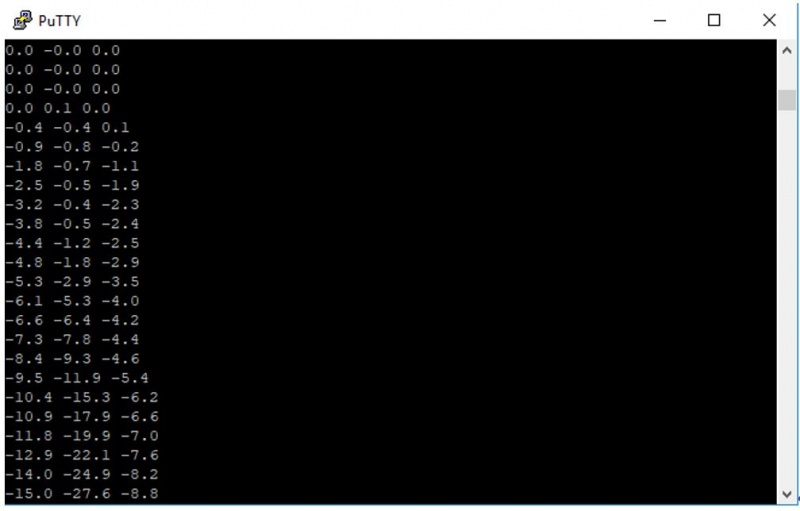
Reading the values
To run the gyroscope, you need to go to the directory where the example code is located.
root@localhost:~# cd /root/linux-academy/2-8
There is a program in C language gyro-i2c.c that calibrates and reads L3GD20 gyroscope:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/i2c-dev.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
/* L3GD20 internal registers */
#define WHO_AM_I 0x0F
#define CTRL_REG1 0x20
#define CTRL_REG2 0x21
#define CTRL_REG3 0x22
#define CTRL_REG4 0x23
#define CTRL_REG5 0x24
#define REFERENCE 0x25
#define OUT_TEMP 0x26
#define STATUS_REG 0x27
#define OUT_X_L 0x28
#define OUT_X_H 0x29
#define OUT_Y_L 0x2A
#define OUT_Y_H 0x2B
#define OUT_Z_L 0x2C
#define OUT_Z_H 0x2D
#define FIFO_CTRL_REG 0x2E
#define FIFO_SRC_REG 0x2F
#define INT1_CFG 0x30
#define INT1_SRC 0x31
#define INT1_TSH_XH 0x32
#define INT1_TSH_XL 0x33
#define INT1_TSH_YH 0x34
#define INT1_TSH_YL 0x35
#define INT1_TSH_ZH 0x36
#define INT1_TSH_ZL 0x37
#define INT1_DURATION 0x38
#define GYRO_ADDR 0x6b
#define AUTO_INCREMENT 0x80
/* calibration values */
int x_low = 0, y_low = 0, z_low = 0;
int x_high = 0, y_high = 0, z_high = 0;
/*
* get_timestamp
*/
static unsigned long
get_timestamp ()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday (&tv,NULL);
return tv.tv_sec * 1000000UL + tv.tv_usec;
}
/*
* gyro_init
*/
static int
gyro_init (int i2c_fd)
{
unsigned char init_seq[6];
init_seq[0] = (CTRL_REG1 | AUTO_INCREMENT);
init_seq[1] = 0xCF; /* CTRL_REG1: normal mode, xyz enable */
init_seq[2] = 0x01; /* CTRL_REG2: <default value> */
init_seq[3] = 0x00; /* CTRL_REG3: <default value> */
init_seq[4] = 0x80; /* CTRL_REG4: 250dps, Block Data Update */
init_seq[5] = 0x02; /* CTRL_REG5: <default value> */
if (write (i2c_fd, init_seq, 6) != 6)
return -1;
return 0;
}
/*
* gyro_get_status
*/
static int
gyro_get_status (int i2c_fd)
{
unsigned char reg_addr = STATUS_REG;
unsigned char reg_data[1];
int ret;
struct i2c_msg messages[] =
{
{
GYRO_ADDR, /* slave address */
0, /* flags: 0 */
sizeof(reg_addr), /* transfer size */
®_addr /* data */
},
{
GYRO_ADDR, /* slave adddress */
I2C_M_RD, /* flags: READ */
sizeof(reg_data), /* transfer size */
reg_data /* data */
}
};
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data packets =
{
messages, /* address of messages */
sizeof(messages) / sizeof(struct i2c_msg) /* number of messages */
};
ret = ioctl (i2c_fd, I2C_RDWR, &packets);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
return (reg_data[0] & (1 << 3));
}
/*
* gyro_get_xyz
*/
static int
gyro_get_xyz (int i2c_fd, float *x, float *y, float *z)
{
unsigned char reg_addr = OUT_X_L | AUTO_INCREMENT;
unsigned char reg_data[6];
int ret;
struct i2c_msg messages[] =
{
{
GYRO_ADDR, /* slave address */
0, /* flags: 0 */
sizeof(reg_addr), /* transfer size */
®_addr /* data */
},
{
GYRO_ADDR, /* slave adddress */
I2C_M_RD, /* flags: READ */
sizeof(reg_data), /* transfer size */
reg_data /* data */
}
};
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data packets =
{
messages, /* address of messages */
sizeof(messages) / sizeof(struct i2c_msg) /* number of messages */
};
ret = ioctl (i2c_fd, I2C_RDWR, &packets);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
*x = (short) (reg_data[0] + ((short)reg_data[1] << 8));
*y = (short) (reg_data[2] + ((short)reg_data[3] << 8));
*z = (short) (reg_data[4] + ((short)reg_data[5] << 8));
return 0;
}
/*
* gyro_calib
*/
static int
gyro_calib (int i2c_fd)
{
float x_raw, y_raw, z_raw;
int ret;
for (int i =0 ; i < 200 ; i++)
{
/* check when a new set of data is available */
while (!gyro_get_status (i2c_fd));
/* read xyz raw values */
ret = gyro_get_xyz (i2c_fd, &x_raw, &y_raw, &z_raw);
if (ret < 0)
break;
/* thresholds for x-axis */
if (x_raw > x_high)
x_high = x_raw;
else if (x_raw < x_low)
x_low = x_raw;
/* thresholds for y-axis */
if (y_raw > y_high)
y_high = y_raw;
else if (y_raw < y_low)
y_low = y_raw;
/* thresholds for z-axis */
if (z_raw > z_high)
z_high = z_raw;
else if (z_raw < z_low)
z_low = z_raw;
}
return ret;
}
/*
* main
*/
int
main (void)
{
int i2c_fd, ret;
float x_raw, y_raw, z_raw;
unsigned long pt = 0;
/* actual angles */
float angX = 0;
float angY = 0;
float angZ = 0;
/* previous angles for calculation */
float p_angX = 0;
float p_angY = 0;
float p_angZ = 0;
/* open i2c device */
i2c_fd = open ("/dev/i2c-1", O_RDWR);
if (i2c_fd < 0)
{
printf ("Failed to open the i2c bus\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
/* set slave address */
ret = ioctl (i2c_fd, I2C_SLAVE, GYRO_ADDR);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf ("Failed to acquire bus access and/or talk to slave\n");
goto exit;
}
/* gyro init */
ret = gyro_init (i2c_fd);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf ("gyro_init error!\n");
goto exit;
}
/* gyro calib */
puts ("Calibration...");
ret = gyro_calib (i2c_fd);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf ("gyro_calib error!\n");
goto exit;
}
/* infinite loop */
while (1)
{
/* check when a new set of data is available */
while (!gyro_get_status (i2c_fd));
/* read xyz raw values */
gyro_get_xyz (i2c_fd, &x_raw, &y_raw, &z_raw);
/* get timestamp */
unsigned long ct = get_timestamp();
if (pt == 0)
{
pt = get_timestamp();
continue;
}
float dt = (float) (ct - pt) / 1000000.0;
pt = get_timestamp();
/* x-axis */
if (x_raw >= x_high || x_raw <= x_low)
{
angX += ((p_angX + (x_raw * 0.00875))/2) * dt;
p_angX = x_raw * 0.00875;
}
else
p_angX = 0;
/* y-axis */
if (y_raw >= y_high || y_raw <= y_low)
{
angY += ((p_angY + (y_raw * 0.00875))/2) * dt;
p_angY = y_raw * 0.00875;
}
else
p_angY = 0;
/* z-axis */
if (z_raw >= z_high || z_raw <= z_low)
{
angZ += ((p_angZ + (z_raw * 0.00875))/2) * dt;
p_angZ = z_raw * 0.00875;
}
else
p_angZ = 0;
printf ("%.1f %.1f %.1f\n", angX, angY, angZ);
fflush (stdout);
}
exit:
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
root@localhost:~/linux-academy/2-8# gh || z_raw <= z_low)
-bash: syntax error near unexpected token `)'
, angX, angY, angZ);
fflush (stdout);
}
exit:
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
To compile the program just type:
gcc gyro-i2c.c -o gyro-i2c
Now, it's time to run the application. The readings of three axis values from L3HGD20 chip will be displayed after executing:
root@localhost:~/linux-academy/2-8# ./gyro-i2c
Any move of the sensor board will be related with the readings changes: